The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved lanadelumab (Takhzyro, Shire), the first monoclonal antibody to help prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in patients aged 12 years and older with types I and II HAE.
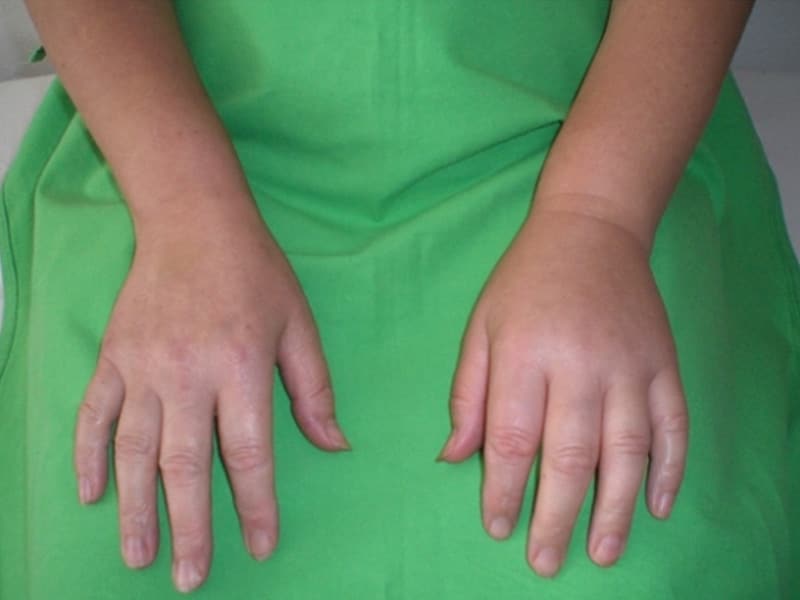
HAE is a rare and potentially life-threatening genetic disorder linked to a defect in the C1-esterase inhibitor protein. The disorder, which affects an estimated 1 in 50,000 men and women, is characterized by relapsing, self-limiting episodes of edema that occur primarily in the extremities, intestinal tract, face, and larynx. Swelling of the airway is potentially fatal unless treated immediately.
Lanadelumab provides targeted inhibition of plasma kallikrein, an enzyme that is chronically uncontrolled in people with HAE, to help prevent attacks.
In the phase 3 Hereditary Angioedema Long-term Prophylaxis (HELP) study of 125 patients with HAE, patients treated with lanadelumab had "clinically meaningful and statistically significant" reductions in the rate of investigator-confirmed HAE attacks compared to patients who received placebo over a 6-month treatment period, the FDA said in a news release announcing the drug's approval.
In comparison with placebo, lanadelumb reduced the number of monthly HAE attacks an average of 87% when administered at a dosage of 300 mg every 2 weeks and by an average of 73% when administered at a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks, Shire said in a news release.
The most common adverse drug reactions are injection site reactions, upper respiratory infections, headache, rash, muscle pain, dizziness, and diarrhea.
"HAE attacks are painful, debilitating, and potentially life threatening. Takhzyro provides the HAE community with a new option for the prevention of HAE attacks," Anthony Castaldo, president, US Hereditary Angioedema Association, said in the release. "We are grateful for the time and effort put forth by the patients and researchers who participated in the clinical trial program that enabled this important addition to the HAE treatment landscape."
Lanadelumab received priority review and breakthrough therapy designation, as well as orphan drug designation.
The recommended starting dosage of lanadelumab is 300 mg every 2 weeks. A dosing interval of 300 mg every 4 weeks is also effective and may be considered if the patient is attack free for more than 6 months. Lanadelumab is a self-administered subcutaneous injection. Full prescribing information is available online.
For more news, join us on Facebook and Twitter
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/901177Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "FDA OKs New Prophylactic Drug for Rare Hereditary Angioedema"
Post a Comment